Spaghetti Models

Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecasts, are a type of statistical model used to make predictions about future events. They are created by running a computer model multiple times with slightly different initial conditions. The resulting set of model runs is then used to create a probability distribution of possible outcomes.
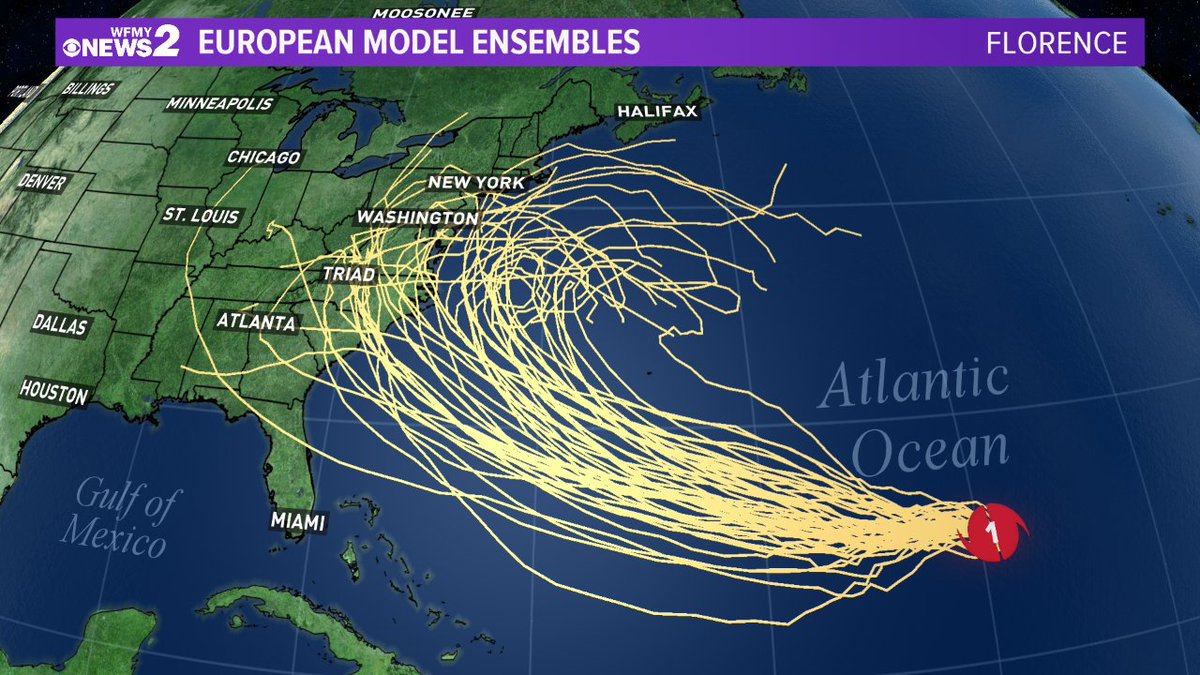
Spaghetti models help us track hurricanes, like Barbados Hurricane Beryl. These models show different possible paths a hurricane could take, kinda like a bunch of spaghetti noodles. By looking at all the different paths, we can get a better idea of where a hurricane might go and how to prepare.
Spaghetti models are often used in weather forecasting, where they can help to predict the path of a hurricane or the likelihood of rain. They can also be used in other fields, such as finance, economics, and epidemiology.
Spaghetti models can provide valuable insights into complex systems. For instance, they have been used to study the spread of diseases in Puerto Rico. By simulating the movement of individuals and the transmission of infection, these models can help identify areas at risk and develop effective containment strategies.
Spaghetti models are a powerful tool that can be used to gain a better understanding of a wide range of phenomena.
Advantages of Spaghetti Models
- Spaghetti models can help to reduce uncertainty in predictions.
- They can provide a more comprehensive view of the possible outcomes of an event.
- They can be used to identify potential risks and opportunities.
Disadvantages of Spaghetti Models
- Spaghetti models can be computationally expensive to run.
- They can be difficult to interpret.
- They can be sensitive to the initial conditions of the model.
Examples of Spaghetti Models
- The National Hurricane Center uses spaghetti models to predict the path of hurricanes.
- The Federal Reserve uses spaghetti models to predict economic growth.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention uses spaghetti models to predict the spread of infectious diseases.
Types of Spaghetti Models
![]()
Spaghetti models are a type of statistical model used to forecast future events. They are called “spaghetti models” because the lines on the graph representing the different forecasts look like spaghetti. There are three main types of spaghetti models: linear, nonlinear, and mixed-effects models.
Linear Spaghetti Models
Linear spaghetti models assume that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is linear. This means that the line on the graph representing the forecast will be a straight line. Linear spaghetti models are relatively simple to fit and interpret, and they are often used when the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is thought to be linear.
Nonlinear Spaghetti Models
Nonlinear spaghetti models assume that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is nonlinear. This means that the line on the graph representing the forecast will not be a straight line. Nonlinear spaghetti models are more complex to fit and interpret than linear spaghetti models, but they can be more accurate when the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is nonlinear.
Mixed-Effects Spaghetti Models
Mixed-effects spaghetti models are a combination of linear and nonlinear spaghetti models. They assume that the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is linear for some observations and nonlinear for others. Mixed-effects spaghetti models are more complex to fit and interpret than linear or nonlinear spaghetti models, but they can be more accurate when the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is complex.
| Type of Spaghetti Model | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | Straight line | Relationships that are thought to be linear |
| Nonlinear | Not a straight line | Relationships that are thought to be nonlinear |
| Mixed-Effects | Combination of linear and nonlinear | Relationships that are complex |
Creating and Interpreting Spaghetti Models
Creating and interpreting spaghetti models involves several steps. Understanding the statistical assumptions and limitations of these models is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Creating Spaghetti Models
To create a spaghetti model:
- Gather Data: Collect historical data relevant to the forecasting problem.
- Choose Forecast Horizon: Determine the time period for which forecasts are desired.
- Simulate Scenarios: Run multiple simulations of the model, each with different random inputs, to generate a range of possible outcomes.
- Plot Results: Display the simulated outcomes as a spaghetti plot, with each line representing a different scenario.
Statistical Assumptions
Spaghetti models assume:
- The underlying process is stochastic and follows a known probability distribution.
- The parameters of the distribution are constant over the forecast horizon.
- The scenarios are independent and do not influence each other.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of the model depends on the validity of the assumptions and the quality of the data.
- Complexity: The model can become complex and difficult to interpret with a large number of scenarios.
- Assumptions: The assumptions may not always hold true in real-world situations.
- Central Tendency: Examine the median or mean of the simulated outcomes to identify the most likely forecast.
- Uncertainty: Assess the spread of the spaghetti plot to understand the range of possible outcomes.
- Outliers: Identify any extreme scenarios that deviate significantly from the majority.
- Probability: The frequency of occurrence of each scenario can be used to estimate the probability of different outcomes.
Limitations
Limitations of spaghetti models include:
Interpreting Results
To interpret the results of a spaghetti model: